Bluetooth 5 wireless technology for IoT smart sensor
Smart sensors with Bluetooth interfaces are increasingly using the cloud in the course of the transition to more connectivity. The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) relies upon sensors to collect data from systems to monitor pressure, movement, humidity and other functions that can be fed into the cloud for processing. Whilst there are several ways to communicate, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is one of the simplest.
BLE can be used in a variety of applications including areas such as: to detect the proximity of two paired devices and report if they go out of range and verified access to devices and, also medical field applications whereby a wide range of body parameters can be monitored, plus smart home automation, in which all devices, doors and windows are connected to a smartphone or a central controller to make life easier. BLE also works well on energy-saving fitness machines and smart bands.
There is considerable enthusiasm around the vision of a smart city / campus, whereby sensors attached to objects such as garbage cans, vending machines and cafeteria seats provide continuous reports about their status. Such as the level of utilization of a dustbin, garbage, or indicating if a seat is occupied. Advances in miniaturization allow them to be implemented into almost any environment, in various form factors and on different objects.
Smart community
'Smart Homes' and 'Smart Buildings' are one of the most important IoT applications in which embedded sensors and actuators may be configured and remotely controlled via the Internet with a variety of monitoring and control programs. ‘Smart Building’ is made possible through the use of smart sensors that can communicate with each other and also with a central monitor or smartphone. With the smart building system, parameters such as the temperature and status of doors and windows can be controlled and each device can be switched on or off from anywhere. This plays a very important role for more security and a comfortable life.
The smart system is made up of the following types of components
- A network of sensors continuously monitors all rooms in the building for parameters such as light intensity, temperature and air quality. Some sensors monitor the exterior of the building for break-ins.
- Services include all the various devices that affect the inside or outside of the building, including essentials like lighting, heating, and water heating, as well as amenities provided for comfort such as the entire building audio system.
- A hub is a processor in the middle of the network, it runs an algorithm that uses data from multiple sources to determine how best to use the service. These services send usage data to the hub, which it uses to identify any initial maintenance issues. The centre also has access to external data sources such as weather forecasts in order to determine whether water from the grid or solar thermal energy on the roof should be heated at sunrise.
- The connections link sensors, services and interfaces to the hub and communicates between them. This is where Bluetooth comes in.
Bluetooth 5 for smart community
For smart IoT deployment in a residential neighborhood or apartment complex, conventional automation methods use a large number of repeaters and devices to connect devices to the central control device, or the Internet. There are limitations though with direct Internet connectivity of Bluetooth devices and also range limitations. These limitations are overcome by using BLE mesh network as shown in figure 1. The proposed new technology only requires a single central gateway to the Internet for an entire residential complex or apartment complex or shopping center. This helps reduce the cost of implementation, as all houses or apartments can be easily monitored using a single central monitoring device. Increasing the number of smart devices in every home can greatly increase the uses of smart building automation, from security to healthcare.
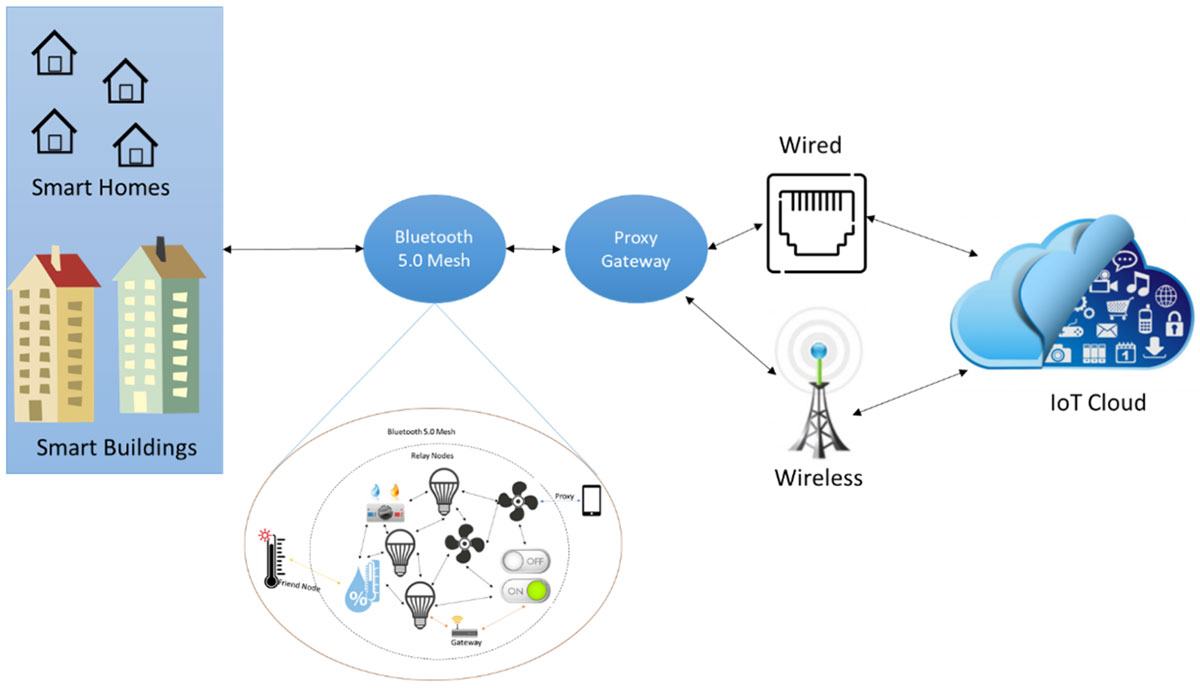
Figure 1: Bluetooth 5 for smart community
The most important feature of Bluetooth now is the Bluetooth mesh topology that enables communication between multiple devices and is optimized for creating large-scale device networks. The mesh network works in BLE and is compatible with version 4.0 and higher of the main specification. It offers true industrial grade solutions on the strict expectations of reliability, scalability and security. Unlike a point-to-point connection, a mesh network is made up of devices that can communicate with all other devices on the network by exchanging messages. In the Bluetooth mesh protocol, each sensor and service acts as a node, transmitting messages between the hub and other sensors and services.
These sensors can be temperature, light intensity, humidity. The nodes can also be used for example to track door condition in a building and can control fan/AC, lamps and is also capable of giving security alert. The system can be controlled locally via smartphone acting as a proxy node or through internet via a proxy gateway.
Messages are passed from one node to another (relay) so that messages can be exchanged between nodes that are not in a direct range of each other. In addition, the messages are transmitted to various devices. The general benefit of mesh networks is that they offer greater fault tolerance to node failures in parts of the network. The smart sensor should be connected to the BLE nodes such as nrf52840 module, BlueNRG , CYBT-213043-MESH etc.
The main advantages of the mesh architecture include a significant reduction in power consumption and operating costs. This is achieved by reducing the number of repeaters used, plus the ability to connect directly to the Internet and other devices on a larger scale compared to other similar architectures. In all intelligent automation systems, repeaters increase the total energy consumption and require more maintenance. Internet portals that support Bluetooth 5 are required to take full advantage of the potential features of the proposed architecture.
For additional information on smart sensors and key trends in sensor development, read our whitepaper on Smart Sensor-enabling the intelligent Internet of Things'.
Stay informed
Keep up to date on the latest information and exclusive offers!
Subscribe now
Thanks for subscribing
Well done! You are now part of an elite group who receive the latest info on products, technologies and applications straight to your inbox.






